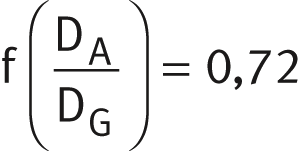Internal clearance and operating clearance
Operating clearance of spherical plain bearings
The operating clearance or preload is determined on a fitted bearing still warm from operation.
It is derived from the radial internal clearance and the change in the radial internal clearance as a result of interference fit and thermal influences in the fitted condition.
Internal clearance of radial spherical plain bearings
The radial and axial internal clearance is determined on the dismounted bearing.
The radial internal clearance of radial spherical plain bearings is defined as the distance by which the inner ring can be moved in a radial direction relative to the outer ring from one extreme position to the precisely opposite extreme position, ➤ Figure.
Maintenance-free spherical plain bearings
Maintenance-free spherical plain bearings have a very small internal clearance. As a result, preloads may be present once the bearing is fitted.
Spherical plain bearings requiring maintenance
The radial internal clearance is subdivided into three groups in accordance with DIN ISO 12240-1, see table. The precondition is a housing bore that causes no dimensional changes in the bearing with the exception of geometrical inaccuracies.
Radial internal clearance

Radial internal clearance groups
Internal clearance group in accordance with ISO 12240-1 | Description | Application range |
|---|---|---|
Group N (CN) | Normal internal clearance; CN is not included in bearing designations | Under normal operating |
(C2) | Internal clearance < CN | For bearing arrangements |
Group 3 (C3) | Internal clearance > CN | For bearing rings with press fits or |
**Relubrication only possible with tilt angle α = 0°.
**Example of bearing with restricted internal clearance: GE220-DO-2RS-C2.
Radial internal clearance
Series | Radial internal clearance | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
μm | |||||||
GE..-DO | GE..-FO | Group 2 | Group N | Group 3 | |||
Bore d | |||||||
mm | min. | max. | min. | max. | min. | max. | |
6 | 6 | 8 | 32 | 32 | 68 | 68 | 104 |
8 | 8 | 8 | 32 | 32 | 68 | 68 | 104 |
10 | 10 | 8 | 32 | 32 | 68 | 68 | 104 |
12 | ‒ | 8 | 32 | 32 | 68 | 68 | 104 |
‒ | 12 | 10 | 40 | 40 | 82 | 82 | 124 |
15 | 15 | 10 | 40 | 40 | 82 | 82 | 124 |
16 | ‒ | 10 | 40 | 40 | 82 | 82 | 124 |
17 | 17 | 10 | 40 | 40 | 82 | 82 | 124 |
20 | ‒ | 10 | 40 | 40 | 82 | 82 | 124 |
‒ | 20 | 12 | 50 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 150 |
25 | 25 | 12 | 50 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 150 |
30 | 30 | 12 | 50 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 150 |
32 | ‒ | 12 | 50 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 150 |
35 | ‒ | 12 | 50 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 150 |
‒ | 35 | 15 | 60 | 60 | 120 | 120 | 150 |
40 | 40 | 15 | 60 | 60 | 120 | 120 | 180 |
45 | 45 | 15 | 60 | 60 | 120 | 120 | 180 |
50 | 50 | 15 | 60 | 60 | 120 | 120 | 180 |
60 | ‒ | 15 | 60 | 60 | 120 | 120 | 180 |
‒ | 60 | 18 | 72 | 72 | 142 | 142 | 212 |
63 | ‒ | 18 | 72 | 72 | 142 | 142 | 212 |
70 | 70 | 18 | 72 | 72 | 142 | 142 | 212 |
80 | 80 | 18 | 72 | 72 | 142 | 142 | 212 |
90 | ‒ | 18 | 72 | 72 | 142 | 142 | 212 |
‒ | 90 | 18 | 85 | 85 | 165 | 165 | 245 |
100 | 100 | 18 | 85 | 85 | 165 | 165 | 245 |
110 | 110 | 18 | 85 | 85 | 165 | 165 | 245 |
120 | 120 | 18 | 85 | 85 | 165 | 165 | 245 |
140 | ‒ | 18 | 85 | 85 | 165 | 165 | 245 |
160 | 140 | 18 | 100 | 100 | 192 | 192 | 284 |
180 | 160 | 18 | 100 | 100 | 192 | 192 | 284 |
200 | 180 | 18 | 100 | 100 | 192 | 192 | 284 |
‒ | 200 | 18 | 110 | 110 | 214 | 214 | 318 |
220 | 220 | 18 | 110 | 110 | 214 | 214 | 318 |
240 | ‒ | 18 | 110 | 110 | 214 | 214 | 318 |
250 | 240 | 18 | 125 | 125 | 239 | 239 | 353 |
260 | 260 | 18 | 125 | 125 | 239 | 239 | 353 |
280 | 280 | 18 | 125 | 125 | 239 | 239 | 353 |
300 | ‒ | 18 | 125 | 125 | 239 | 239 | 353 |
Axial internal clearance
The axial internal clearance is defined as the distance by which the inner ring can be moved in an axial direction relative to the outer ring from one extreme position to the precisely opposite extreme position, ➤ Figure.
It is dependent on the bearing geometry and is in a direct relationship with the radial internal clearance. Depending on the bearing type, it may be several times greater than the radial internal clearance.
Axial internal clearance

Fit conditions for spherical plain bearings
The interference fits and clearance fits for practical use are determined from the corresponding ISO fit in conjunction with the normal bearing tolerances in accordance with DIN ISO 12240-1 to DIN ISO 12240-3, see tables. The actual dimensions must correspond to the centre tolerance.
Definitions:
- – indicates an interference fit
- + indicates a clearance fit.
Shaft fits
Example:
- A shaft of diameter ⌀50 m6 Ⓔ has a probable interference fit of 0,023 mm.
Interference fit ÜI or clearance fit
Nominal shaft diameter in mm | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
over incl. | 3 6 | 6 10 | 10 18 | 18 30 | 30 50 | 50 80 | 80 120 | 120 180 | 180 250 | 250 315 | 315 400 | 400 500 |
Normal tolerance, interference fit or clearance fit in μm** | ||||||||||||
h6 | 0 | 0 | +1 | +1 | +2 | +2 | +1 | 0 | 0 | –2 | –2 | –2 |
j6 | –6 | –7 | –7 | –8 | –9 | –10 | –13 | –14 | –17 | –17 | –20 | –22 |
k6 | –9 | –9 | –9 | –14 | –16 | –20 | –24 | –28 | –30 | –33 | –38 | –42 |
m6 | –12 | –15 | –17 | –20 | –23 | –28 | –34 | –40 | –47 | –53 | –59 | –65 |
n6 | –16 | –19 | –22 | –27 | –31 | –37 | –44 | –52 | –61 | –67 | –75 | –82 |
**Not applicable to series GE..-LO, GE..-PB, GE..-SX, GE..-PW and GE..-SW.
Housing fits
Example:
- A housing bore of diameter ⌀75 M7 Ⓔ has a probable interference fit of 0,009 mm.
Interference fit ÜA or clearance fit
Nominal housing bore diameter in mm | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
over incl. | 6 10 | 10 18 | 18 30 | 30 50 | 50 80 | 80 120 | 120 150 | 150 180 | 180 250 | 250 315 | 315 400 | 400 500 |
Normal tolerance, interference fit or clearance fit in μm** | ||||||||||||
J7 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | +10 | +12 | +15 | +18 | +22 | +27 | +31 | +34 |
K7 | +1 | +1 | –1 | 0 | 0 | –1 | +1 | +4 | +5 | +7 | +8 | +8 |
M7 | –4 | –5 | –7 | –8 | –9 | –11 | –11 | –8 | –8 | –9 | –9 | –10 |
N7 | –8 | –10 | –14 | –16 | –18 | –21 | –23 | –20 | –22 | –23 | –25 | –27 |
**Not applicable to series GE..-SX and GE..-SW.
Influence of interference fit
The radial internal clearance of radial spherical plain bearings changes due to the fit as a result of:
- expansion of the inner ring
- contraction of the outer ring.
ACHTUNG
If the remaining internal clearance of spherical plain bearings requiring maintenance is ≦ 0, a bearing of another internal clearance group with a larger internal clearance must be selected.
Factors for expansion or contraction

b = inner ring · c = outer ring · f = factor for expansion of the housing
Expansion of the inner ring

| a | μm | Expansion of the inner ring when using solid shafts, measured on the sphere diameter |
| ÜI | μm | Effective interference fit, see table |
| b | – | Factor for the cross-section of the inner ring, see table, and ➤ Figure |
| 0,9 | – | Factor for the roughness, ovality and unevenness of the supporting component surface. |
Contraction of the outer ring
In the case of ring-shaped housings, expansion of the housing must be taken into consideration. The expansion is dependent on the wall thickness and is taken into consideration in the factor f:
| e | μm | Contraction of the outer ring, measured on the raceway diameter |
| ÜA | μm | Effective interference fit, see table |
| f | – | Factor for expansion of the housing, see link |
| 0,9 | – | Factor for the roughness, ovality and unevenness of the supporting component surface. |
Factor for the cross-section of the inner ring
Bore d | Factor for series b | ||
|---|---|---|---|
mm | |||
from | to | GE..-DO(-2RS), (-2TS) | GE..-FO(-2RS), (-2TS) |
6 | 10 | 0,65 | 0,55 |
12 | 20 | 0,72 | 0,64 |
25 | 70 | 0,79 | 0,71 |
80 | 140 | 0,8 | 0,75 |
160 | 300 | 0,84 | 0,78 |
**Interference fit ÜI not listed in the overview, see table.
Factor for the cross-section of the outer ring
Bore d | Factor for series c | ||
|---|---|---|---|
mm | |||
from | to | GE..-DO(-2RS), (-2TS) | GE..-FO(-2RS), (-2TS) |
‒ | 6 | 0,7 | ‒ |
6 | 20 | ‒ | 0,81 |
8 | 25 | 0,81 | ‒ |
25 | 35 | ‒ | 0,83 |
30 | 40 | 0,83 | ‒ |
40 | 280 | ‒ | 0,85 |
45 | 300 | 0,85 | ‒ |
Calculation of the factor f for expansion of the housing
When determining the factor f, the cross-section of the bearing ring and the ring thickness of the bearing locating housing are taken into consideration, ➤ Figure and ➤ Figure.
Housing ring thickness

Factor f for expansion of the housing

Calculation example for internal clearance
The internal clearance of a radial spherical plain bearing in the fitted condition is calculated using the influence of the interference fit, see link.
Given data
Radial spherical plain bearing GE50-DO with steel/steel sliding contact surface:
Fit between locating bore and shaft | M7/m6 | ||
Outside diameter of housing | ⌀ | 120 mm | |
Solid steel shaft | ⌀ | 50 |
|
Locating bore | ⌀ | 75 |
|
Radial internal clearance Group N | 60 μm to 120 μm | ||
Required
- Radial internal clearance in fitted condition.
Assumption
- Production to centre of tolerance.
Expansion of the inner ring
Expansion of the inner ring, measured on the sphere diameter:
Contraction of the outer ring
Contraction of the outer ring, measured on the raceway diameter:
Reduction in radial internal clearance
The reduction in the radial internal clearance is calculated by adding a and e:
ΔC | = | a + e |
= | 0,016 mm + 0,006 mm | |
= | 0,022 mm. |
Maximum restriction of internal clearance
Maximum possible restriction of radial internal clearance with production to acceptable values:
Solid steel shaft | ⌀ 50,025 mm |
Bearing bore | ⌀ 49,988 mm |
ÜI max | = 0,037 mm |
amax | = ÜI max · b · 0,9 = 0,037 mm · 0,79 · 0,9 |
amax | = 0,026 mm. |
| |
Locating bore | ⌀ 74,97 mm |
Bearing outside diameter | ⌀ 75 mm |
ÜA max | = 0,03 mm |
emax | = ÜA max · f · 0,9 = 0,03 mm · 0,72 · 0,9 |
emax | = 0,019 mm |
Maximum reduction in internal clearance
Maximum reduction in the internal clearance in the fitted condition:
- ΔCmax = amax + emax = 0,026 + 0,019 = 0,045 mm.
The radial internal clearance in the unfitted condition is 0,06 mm to 0,12 mm. The smallest possible initial clearance is 0,06 mm:
- minimum internal clearance = 0,060 mm – 0,045 mm = 0,015 mm.
The internal clearance in the fitted condition in the least favourable case is 0,015 mm.
Theoretical bearing clearance of metal/polymer composite plain bushes
Bushes with the sliding layer E40 and E50 are pressed into the housing. This provides axial and radial location. No additional means of location are required.
If the recommended mounting tolerances are used with rigid housings and shafts, this gives an interference fit or bearing clearance.
ACHTUNG
Expansion of the housing bore is not taken into account in calculation of the bearing clearance.
Calculation of the interference U is carried out using the tolerances of the housing bore and the deviations for the bush outside diameter Do.
Calculation of bearing clearance
The theoretical bearing clearance is calculated as follows:

| Δsmax | mm | Maximum bearing clearance, ➤ Figure |
| Δsmin | mm | Minimum bearing clearance, ➤ Figure |
| dG max | mm | Maximum diameter of housing bore |
| dG min | mm | Minimum diameter of housing bore |
| dW max | mm | Maximum shaft diameter |
| dW min | mm | Minimum shaft diameter |
| s3 max | mm | Maximum wall thickness |
| s3 min | mm | Maximum wall thickness. |
Theoretical bearing clearance

Theoretical bearing clearance
after pressing in
The theoretical bearing clearance after pressing in of bushes or flanged bushes of metric sizes or inch sizes is calculated without considering any possible expansion of the bore, see tables.
The theoretical bearing clearance is calculated taking account of the recommended mounting tolerances.
Theoretical bearing clearance
for metric sizes
Diameter of bush | Bearing clearance Δs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
E40, E40-B | E50 | ||||
Di | Do | Δsmin | Δsmax | Δsmin | Δsmax |
mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm |
3 | 4,5 | 0,000 | 0,054 | ‒ | ‒ |
4 | 5,5 | 0,000 | 0,056 | ‒ | ‒ |
5 | 7 | 0,000 | 0,077 | ‒ | ‒ |
6 | 8 | 0,000 | 0,077 | ‒ | ‒ |
7 | 9 | 0,003 | 0,083 | ‒ | ‒ |
8 | 10 | 0,003 | 0,083 | 0,040 | 0,127 |
10 | 12 | 0,003 | 0,086 | 0,040 | 0,130 |
12 | 14 | 0,006 | 0,092 | 0,040 | 0,135 |
13 | 15 | 0,006 | 0,092 | 0,040 | 0,135 |
14 | 16 | 0,006 | 0,092 | 0,040 | 0,135 |
15 | 17 | 0,006 | 0,092 | 0,040 | 0,135 |
16 | 18 | 0,006 | 0,092 | 0,040 | 0,135 |
18 | 20 | 0,006 | 0,095 | 0,040 | 0,138 |
20 | 23 | 0,010 | 0,112 | 0,050 | 0,164 |
22 | 25 | 0,010 | 0,112 | 0,050 | 0,164 |
24 | 27 | 0,010 | 0,112 | 0,050 | 0,164 |
25 | 28 | 0,010 | 0,112 | 0,050 | 0,164 |
28 | 32 | 0,010 | 0,126 | 0,060 | 0,188 |
30 | 34 | 0,010 | 0,126 | 0,060 | 0,188 |
32 | 36 | 0,015 | 0,135 | 0,060 | 0,194 |
35 | 39 | 0,015 | 0,135 | 0,060 | 0,194 |
40 | 44 | 0,015 | 0,135 | 0,060 | 0,194 |
45 | 50 | 0,015 | 0,155 | 0,080 | 0,234 |
50 | 55 | 0,015 | 0,160 | 0,080 | 0,239 |
Theoretical bearing clearance
for metric sizes
Diameter of bush | Bearing clearance Δs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
E40, E40-B | E50 | ||||
Di | Do | Δsmin | Δsmax | Δsmin | Δsmax |
mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm |
55 | 60 | 0,020 | 0,170 | 0,080 | 0,246 |
60 | 65 | 0,020 | 0,170 | 0,080 | 0,246 |
65 | 70 | 0,020 | 0,170 | 0,080 | 0,246 |
70 | 75 | 0,020 | 0,170 | 0,080 | 0,246 |
75 | 80 | 0,020 | 0,170 | 0,080 | 0,246 |
80 | 85 | 0,020 | 0,201 | 0,080 | 0,251 |
85 | 90 | 0,020 | 0,209 | 0,080 | 0,251 |
90 | 95 | 0,020 | 0,209 | 0,080 | 0,259 |
95 | 100 | 0,020 | 0,209 | 0,080 | 0,259 |
100 | 105 | 0,020 | 0,209 | 0,080 | 0,259 |
105 | 110 | 0,020 | 0,209 | ‒ | ‒ |
110 | 115 | 0,020 | 0,209 | ‒ | ‒ |
115 | 120 | 0,020 | 0,209 | ‒ | ‒ |
120 | 125 | 0,070 | 0,264 | ‒ | ‒ |
125 | 130 | 0,070 | 0,273 | ‒ | ‒ |
130 | 135 | 0,070 | 0,273 | ‒ | ‒ |
135 | 140 | 0,070 | 0,273 | ‒ | ‒ |
140 | 145 | 0,070 | 0,273 | ‒ | ‒ |
150 | 155 | 0,070 | 0,273 | ‒ | ‒ |
160 | 165 | 0,070 | 0,273 | ‒ | ‒ |
180 | 185 | 0,070 | 0,279 | ‒ | ‒ |
200 | 205 | 0,070 | 0,288 | ‒ | ‒ |
220 | 225 | 0,070 | 0,288 | ‒ | ‒ |
250 | 255 | 0,070 | 0,294 | ‒ | ‒ |
300 | 305 | 0,070 | 0,303 | ‒ | ‒ |
Theoretical bearing clearance
for inch sizes
Designation | Nominal diameter | Recommended diameter of | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Shaft | Housing bore | ||||
inch | inch/mm | inch/mm | |||
dW min | dW max | dG min | dG max | ||
EGBZ03 | 3/16 | 0,1858 | 0,1865 | 0,2497 | 0,2503 |
4,719 | 4,737 | 6,342 | 6,358 | ||
EGBZ04 | 1/4 | 0,2481 | 0,2490 | 0,3122 | 0,3128 |
6,302 | 6,325 | 7,930 | 7,945 | ||
EGBZ05 | 5/16 | 0,3106 | 0,3115 | 0,3747 | 0,3753 |
7,889 | 7,912 | 9,517 | 9,533 | ||
EGBZ06 | 3/8 | 0,3731 | 0,3740 | 0,4684 | 0,4691 |
9,477 | 9,500 | 11,897 | 11,915 | ||
EGBZ07 | 7/16 | 0,4355 | 0,4365 | 0,5309 | 0,5316 |
11,062 | 11,087 | 13,485 | 13,503 | ||
EGBZ08 | 1/2 | 0,4980 | 0,4990 | 0,5934 | 0,5941 |
12,649 | 12,675 | 15,072 | 15,090 | ||
EGBZ09 | 9/16 | 0,5605 | 0,5615 | 0,6559 | 0,6566 |
14,237 | 14,262 | 16,660 | 16,678 | ||
EGBZ10 | 5/8 | 0,6230 | 0,6240 | 0,7184 | 0,7192 |
15,824 | 15,850 | 18,247 | 18,268 | ||
EGBZ11 | 11/16 | 0,6855 | 0,6865 | 0,7809 | 0,7817 |
17,412 | 17,437 | 19,835 | 19,855 | ||
EGBZ12 | 3/4 | 0,7479 | 0,7491 | 0,8747 | 0,8755 |
18,997 | 19,027 | 22,217 | 22,238 | ||
EGBZ14 | 7/8 | 0,8729 | 0,8741 | 0,9997 | 1,0005 |
22,172 | 22,202 | 25,392 | 25,413 | ||
EGBZ16 | 1 | 0,9979 | 0,9991 | 1,1246 | 1,1256 |
25,347 | 25,377 | 28,565 | 28,590 | ||
EGBZ18 | 1 1/8 | 1,1226 | 1,1238 | 1,2808 | 1,2818 |
28,514 | 28,545 | 32,532 | 32,558 | ||
EGBZ20 | 1 1/4 | 1,2472 | 1,2488 | 1,4058 | 1,4068 |
31,679 | 31,720 | 35,707 | 35,733 | ||
EGBZ22 | 1 3/8 | 1,3722 | 1,3738 | 1,5308 | 1,5318 |
34,854 | 34,895 | 38,882 | 38,908 | ||
EGBZ24 | 1 1/2 | 1,4972 | 1,4988 | 1,6558 | 1,6568 |
38,029 | 38,070 | 42,057 | 42,083 | ||
EGBZ26 | 1 5/8 | 1,6222 | 1,6238 | 1,7808 | 1,7818 |
41,204 | 41,245 | 45,232 | 45,258 | ||
EGBZ28 | 1 3/4 | 1,7471 | 1,7487 | 1,9371 | 1,9381 |
44,376 | 44,417 | 49,202 | 49,228 | ||
EGBZ32 | 2 | 1,9969 | 1,9987 | 2,1871 | 2,1883 |
50,721 | 50,767 | 55,552 | 55,583 | ||
Theoretical bearing clearance
for inch sizes
Designation | Nominal diameter | Inside diameter | Bearing clearance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
inch/mm | inch/mm | |||||
Di | Do | min. | max. | Δsmin | Δsmax | |
EGBZ03 | 0,1875 | 0,2500 | 0,1867 | 0,1893 | 0,0002 | 0,0035 |
4,763 | 6,350 | 4,742 | 4,808 | 0,005 | 0,089 | |
EGBZ04 | 0,2500 | 0,3125 | 0,2492 | 0,2518 | 0,0002 | 0,0037 |
6,350 | 7,938 | 6,330 | 6,396 | 0,005 | 0,094 | |
EGBZ05 | 0,3125 | 0,3750 | 0,3117 | 0,3143 | 0,0002 | 0,0037 |
7,938 | 9,525 | 7,917 | 7,983 | 0,005 | 0,094 | |
EGBZ06 | 0,3750 | 0,4688 | 0,3742 | 0,3769 | 0,0002 | 0,0038 |
9,525 | 11,906 | 9,505 | 9,573 | 0,005 | 0,096 | |
EGBZ07 | 0,4375 | 0,5313 | 0,4367 | 0,4394 | 0,0002 | 0,0039 |
11,113 | 13,494 | 11,092 | 11,161 | 0,005 | 0,099 | |
EGBZ08 | 0,5000 | 0,5938 | 0,4992 | 0,5019 | 0,0002 | 0,0039 |
12,700 | 15,082 | 12,680 | 12,748 | 0,005 | 0,099 | |
EGBZ09 | 0,5625 | 0,6563 | 0,5617 | 0,5644 | 0,0002 | 0,0039 |
14,288 | 16,669 | 14,267 | 14,336 | 0,005 | 0,099 | |
EGBZ10 | 0,6250 | 0,7188 | 0,6242 | 0,6270 | 0,0002 | 0,0040 |
15,875 | 18,258 | 15,855 | 15,926 | 0,005 | 0,102 | |
EGBZ11 | 0,6875 | 0,7813 | 0,6867 | 0,6895 | 0,0002 | 0,0040 |
17,463 | 19,844 | 17,442 | 17,513 | 0,005 | 0,101 | |
EGBZ12 | 0,7500 | 0,8750 | 0,7493 | 0,7525 | 0,0002 | 0,0046 |
19,050 | 22,225 | 19,032 | 19,114 | 0,005 | 0,116 | |
EGBZ14 | 0,8750 | 1,0000 | 0,8743 | 0,8775 | 0,0002 | 0,0046 |
22,225 | 25,400 | 22,207 | 22,289 | 0,005 | 0,116 | |
EGBZ16 | 1,0000 | 1,1250 | 0,9992 | 1,0026 | 0,0001 | 0,0047 |
25,400 | 28,575 | 25,380 | 25,466 | 0,003 | 0,119 | |
EGBZ18 | 1,1250 | 1,2813 | 1,1240 | 1,1278 | 0,0002 | 0,0052 |
28,575 | 32,544 | 28,550 | 28,646 | 0,005 | 0,132 | |
EGBZ20 | 1,2500 | 1,4063 | 1,2490 | 1,2528 | 0,0002 | 0,0056 |
31,750 | 35,719 | 31,725 | 31,821 | 0,005 | 0,142 | |
EGBZ22 | 1,3750 | 1,5313 | 1,3740 | 1,3778 | 0,0002 | 0,0056 |
34,925 | 38,894 | 34,900 | 34,996 | 0,005 | 0,142 | |
EGBZ24 | 1,5000 | 1,6563 | 1,4990 | 1,5028 | 0,0002 | 0,0056 |
38,100 | 42,069 | 38,075 | 38,171 | 0,005 | 0,142 | |
EGBZ26 | 1,6250 | 1,7813 | 1,6240 | 1,6278 | 0,0002 | 0,0056 |
41,275 | 45,244 | 41,250 | 41,346 | 0,005 | 0,142 | |
EGBZ28 | 1,7500 | 1,9375 | 1,7489 | 1,7535 | 0,0002 | 0,0064 |
44,450 | 49,213 | 44,422 | 44,539 | 0,005 | 0,163 | |
EGBZ32 | 2,0000 | 2,1875 | 1,9989 | 2,0037 | 0,0002 | 0,0068 |
50,800 | 55,563 | 50,772 | 50,894 | 0,005 | 0,173 | |
Interference fit and bearing clearance of metal/polymer composite plain bushes
The table shows measures that can be taken to influence the bearing clearance and interference fit:
- at high ambient temperatures
- depending on housing material
- depending on housing wall thickness.
Reduced clearance tolerances require tighter tolerances for the shaft and the bore.
Consequences and measures due to environmental influences
Consequences and measures for interference fit and bearing clearance in the case of high ambient temperatures, special housing materials or special wall thicknesses, see table.
Environmental influence
Design and environmental influences | Consequences | Measures | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Bearing clearance | Poor interference fit | Change in diameter | ||||
Too large | Too small | dG | dW | Notes | ||
Light metal or thin-walled housings | ■ | ‒ | ‒ | ● | ‒ | The housing is more highly stressed; |
Steel or cast iron housings** | ‒ | ■ | ‒ | ‒ | ▼ | ‒ |
Bronze or copper alloy housings** | ‒ | ‒ | ■ | ▲ | ▲ | Reduce dG and dW by the same |
Aluminium alloy housings** | ‒ | ‒ | ■ | ❍ | ❍ | Reduce dG and dW by the same At temperatures below 0 °C, |
Bushes with thicker anti-corrosion layer | ‒ | ■ | ‒ | ❑ | ‒ | The bush and housing will be more highly stressed if appropriate |
■
Applicable
●
Reduce
❍
Reduce by 0,1% per 100 °C above room temperature
▲
Reduce by 0,05% per 100 °C above room temperature
❑
Increase by 0,03 mm if, for example, the layer thickness = 0,015 mm
▼
Reduce by 0,008 mm per 100 °C above room temperature.
**At high ambient temperatures.
Theoretical bearing clearance of ELGOTEX filament wound bushes
The bushes are pressed as standard into a housing with the tolerance H7. This provides radial and axial location. Due to the contraction of the inside diameter, there is a change in the tolerance of the inside diameter of the bush after pressing in, see table.
ACHTUNG
Expansion of the housing bore is not taken into consideration in calculation of the bearing clearance.


| Δsmax | mm | Maximum bearing clearance |
| Δsmin | mm | Minimum bearing clearance |
| Di max | mm | Maximum inside diameter of bush after pressing in, see table |
| Di min | mm | Minimum inside diameter of bush after pressing in, see table |
| dW min | mm | Minimum shaft diameter |
| dW max | mm | Maximum shaft diameter. |
Theoretical bearing clearance after pressing-in
For a housing tolerance H7 and the recommended shaft tolerance h7, the minimum and maximum theoretical clearances for the standard dimensions are stated, see table. The data do not take account of any possible expansion of the housing bore.
Theoretical bearing clearance for metric sizes
Diameter | Inside diameter | Bearing clearance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Di | Do | Di min | Di max | Δsmin | Δsmax |
mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm |
20 | 24 | 20,042 | 20,18 | 0,042 | 0,201 |
25 | 30 | 25,042 | 25,18 | 0,042 | 0,201 |
28 | 34 | 28,028 | 28,176 | 0,028 | 0,197 |
30 | 36 | 30,028 | 30,176 | 0,028 | 0,197 |
35 | 41 | 35,038 | 35,202 | 0,038 | 0,227 |
40 | 48 | 40,038 | 40,202 | 0,038 | 0,227 |
45 | 53 | 45,031 | 45,207 | 0,031 | 0,232 |
50 | 58 | 50,031 | 50,207 | 0,031 | 0,232 |
55 | 63 | 55,041 | 55,237 | 0,041 | 0,267 |
60 | 70 | 60,035 | 60,231 | 0,035 | 0,261 |
65 | 75 | 65,035 | 65,231 | 0,035 | 0,261 |
70 | 80 | 70,045 | 70,241 | 0,045 | 0,271 |
75 | 85 | 75,025 | 75,234 | 0,025 | 0,264 |
80 | 90 | 80,025 | 80,234 | 0,025 | 0,264 |
85 | 95 | 85,045 | 85,274 | 0,045 | 0,309 |
90 | 105 | 90,037 | 90,266 | 0,037 | 0,301 |
95 | 110 | 95,037 | 95,266 | 0,037 | 0,301 |
100 | 115 | 100,037 | 100,266 | 0,037 | 0,301 |
105 | 120 | 105,047 | 105,276 | 0,047 | 0,311 |
110 | 125 | 110,025 | 110,268 | 0,025 | 0,303 |
120 | 135 | 120,025 | 120,268 | 0,025 | 0,303 |
130 | 145 | 130,037 | 130,3 | 0,037 | 0,34 |
140 | 155 | 140,037 | 140,3 | 0,037 | 0,34 |
150 | 165 | 150,039 | 150,302 | 0,039 | 0,342 |
160 | 180 | 160,039 | 160,302 | 0,039 | 0,342 |
170 | 190 | 170,036 | 170,314 | 0,036 | 0,354 |
180 | 200 | 180,036 | 180,314 | 0,036 | 0,354 |
190 | 210 | 190,038 | 190,341 | 0,038 | 0,387 |
200 | 220 | 200,038 | 200,341 | 0,038 | 0,387 |
Operating clearance of ELGOGLIDE plain bushes
Due to the self-lubricating PTFE fabric, maintenance-free ELGOGLIDE plain bushes do not require a minimum radial clearance determined by lubrication conditions.
Fitting without clearance has particular advantages, especially with alternating load directions. Load distribution is also improved, especially during running-in, due to the larger load-bearing areas.
In order to achieve the largest possible load-bearing angle, the operating clearance s must not exceed defined limits. The clearance can be expressed as a function of the relative bearing clearance ψ, see ➤ equation and ➤ Figure.
The guide values for the relative bearing clearance are valid for shaft diameters d = 30 mm to 200 mm, see table.
The ranges for the operating clearance are achievable with the standard tolerances of the plain bushes and where the housing bore and shaft are manufactured to the central tolerance.
Guide values for relative bearing clearance in fitted condition
Shaft diameter d | Relative bearing clearance ψ | ||
|---|---|---|---|
mm | ‰ | ||
< | 80 | ≦ 1 | |
≧ | 80 | – 120 | ≦ 0,75 |
> | 120 | – 200 | ≦ 0,5 |
Calculation of the operating clearance

| s | μm | Operating clearance, ➤ Figure |
| ψ | ‰ | Relative bearing clearance in fitted condition, see table |
| d | mm | Shaft diameter, bore diameter of inner ring. |
Operating clearance